COMPUTER VISION
COMPUTER VISION
Computer Vision, a branch of artificial intelligence, enables machines to interpret and understand the visual world, mimicking human vision. In this tech blog post, we will delve into the fascinating realm of Computer Vision, exploring its applications and providing concrete examples that highlight its real-time potential.
Computer Vision involves equipping machines with the ability to interpret and make decisions based on visual data. It encompasses a wide range of tasks, from image recognition to video analysis, enabling applications that were once the realm of science fiction.
Applications of Computer Vision
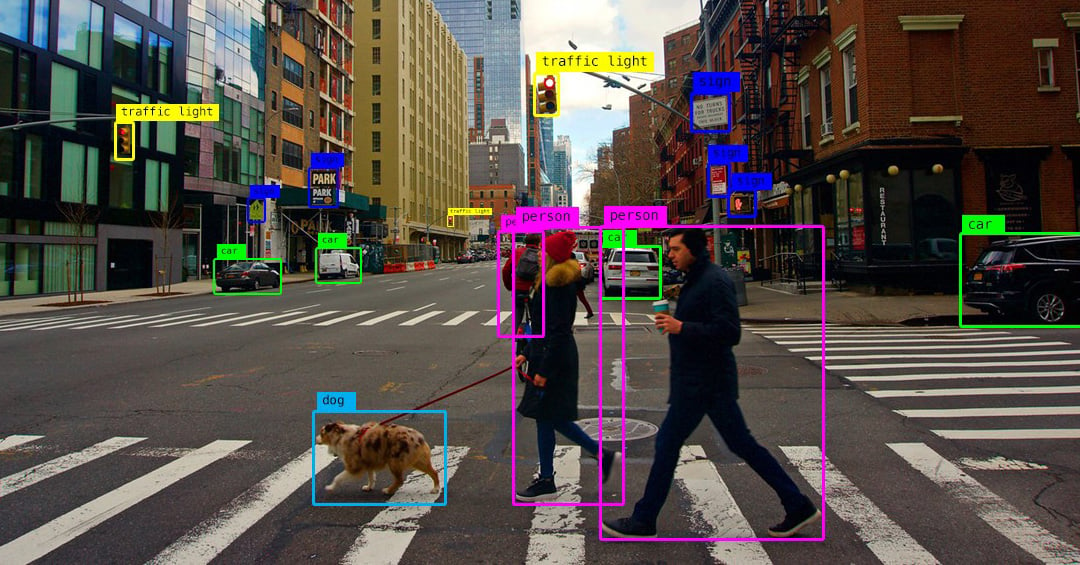
1. Image Recognition and Classification
Example: Identifying Objects in Photos
Computer Vision excels in recognizing and categorizing objects within images. For instance, consider a scenario where an algorithm identifies and classifies various objects in a photograph, such as distinguishing between different animals or recognizing specific items in a retail environment.
2. Face Detection and Recognition
Example: Biometric Security Systems
Face detection and recognition have found applications in security systems, unlocking smartphones, and even enhancing user experience in cameras. Advanced algorithms can accurately detect and identify faces in real-time, contributing to the development of secure access control and authentication mechanisms.
3. Object Tracking in Video
Example: Surveillance and Monitoring
Computer Vision enables real-time object tracking in video streams, crucial for surveillance and monitoring applications. This technology is employed in tracking moving objects, such as vehicles or individuals, in scenarios ranging from traffic management to security systems.
4. Augmented Reality (AR)
Example: Interactive Gaming
Augmented Reality merges computer-generated content with the user's real-world environment. Computer Vision plays a pivotal role in tracking and recognizing physical objects, facilitating interactive gaming experiences where virtual elements seamlessly interact with the real world.
5. Autonomous Vehicles
Example: Self-Driving Cars
Computer Vision is a cornerstone in the development of autonomous vehicles. It enables cars to interpret their surroundings, recognize obstacles, and make real-time decisions for navigation. This technology is crucial for enhancing safety and efficiency in the transportation sector.
Real-Time Applications of Computer Vision
1. Healthcare Imaging
Real-time medical imaging applications, such as identifying anomalies in X-rays or monitoring patient vital signs through computer vision, contribute to faster and more accurate diagnoses.
2. Retail Analytics
In the retail sector, computer vision is employed for real-time inventory tracking, analyzing customer behavior, and enhancing the overall shopping experience through technologies like smart shelves and automated checkout systems.
3. Industrial Automation
Computer Vision is instrumental in industrial settings for quality control, defect detection, and robotic guidance, ensuring high precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Computer Vision is transforming the way we interact with technology, opening doors to a myriad of innovative applications. From image recognition to real-time video analysis, the examples and applications discussed in this blog post showcase the immense potential and real-world impact of Computer Vision. As technology continues to evolve, we can anticipate even more groundbreaking applications that will shape the future of this dynamic field.
PROJECTS
Uusing opencv and python
Before diving into the projects, ensure you have the following prerequisites installed:
Python (3.x recommended)
OpenCV
NumPy
Matplotlib
pip install opencv-python numpy matplotlib
Project 1: Image Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
Objective
Classify images using a pre-trained CNN model and analyze the results.
Steps
Import Libraries:
import cv2
from tensorflow.keras.applications import VGG16
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input, decode_predictions
Load Pre-trained Model:
model = VGG16(weights='imagenet')
Load and Preprocess Image:
img_path = 'path/to/your/image.jpg'
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(224, 224))
img_array = image.img_to_array(img)
img_array = preprocess_input(img_array)
Make Predictions:
predictions = model.predict(img_array.reshape(1, 224, 224, 3))
Display Results:
label = decode_predictions(predictions)
print('Predicted:', label[0][0][1])
Analysis:
Analyze the results and explore the potential of CNN for image classification tasks.
Project 2: Face Detection and Recognition
Objective
Implement a system that can detect and recognize faces in images.
Steps
Import Libraries:
import cv2
import numpy as np
Load Pre-trained Haar Cascade Classifier:
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('path/to/haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
Load and Process Image:
img_path = 'path/to/your/image.jpg'
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
Detect Faces:
faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, scaleFactor=1.1, minNeighbors=5)
Draw Rectangles and Recognize Faces:
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (255, 0, 0), 2)
roi_gray = gray[y:y+h, x:x+w]
# Implement face recognition as needed
Display Results:
cv2.imshow('Face Detection', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Analysis:
Explore the potential applications of face detection and recognition, such as security systems or attendance tracking.
Project 3: Object Tracking in Real-Time Video
Objective
Create a real-time object tracking system using Python and OpenCV.
Steps
Import Libraries:
import cv2
import numpy as np
Capture Video Stream:
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('path/to/your/video.mp4')
Define Object to Track:
_, frame = cap.read()
roi = cv2.selectROI(frame)
Initialize Tracker:
tracker = cv2.TrackerCSRT_create()
tracker.init(frame, roi)
Track Object in Video:
while True:
_, frame = cap.read()
success, roi = tracker.update(frame)
if success:
(x, y, w, h) = tuple(map(int, roi))
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('Object Tracking', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(30) & 0xFF == 27: # Press 'Esc' to exit
break
Release Resources:
python
Copy code
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Analysis:
Discuss the potential applications of real-time object tracking, such as surveillance or augmented reality.
Conclusion
These three computer vision projects showcase the versatility and power of Python, OpenCV, and machine learning in solving real-world problems. As you explore and build upon these projects, you'll gain valuable insights into the exciting world of computer vision. Feel free to adapt and expand these projects to suit your specific needs and interests. Happy coding!



Comments
Post a Comment