THE MUSK THINGS:- TESLA
THE MUSK THINGS
" TESLA "
TODAY LET'S GO WITH "TESLA" IN THE MUSK THINGS SERIES
Tesla, Inc. is an American multinational automotive (AMA) and clean energy company headquartered in Austin, Texas. Tesla designs and manufactures electric vehicles (electric cars and trucks), EVs' battery energy storage from home to grid-scale, solar panels and solar roof tiles, and related products and services mostly known as Tesla Solar Tesla is one of the world's most valuable companies and remains the world's most valuable automaker with a market capitalization of more than US$840 billion. now u people think that wth is happening but we should respect these guys for making a org that propells mankinds state of art tech to next level In 2021, the company had the most worldwide sales of battery electric vehicles and plug-in electric vehicles, capturing 21% of the battery-electric (purely electric) market and 14% of the plug-in market (which includes plug-in hybrids). Through its subsidiary Tesla Energy, the company develops and is a major installer of photovoltaic systems in the United States. Tesla Energy is also one of the largest global suppliers of battery energy storage systems, with 3.99 gigawatt-hours (GWh) installed in 2021. Tesla was incorporated in July 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning as Tesla Motors. The company's name is a tribute to inventor and electrical engineer Nikola Tesla. In February 2004, via a $6.5 million investment, Elon Musk became the largest shareholder of the company. He has served as CEO since 2008. According to Musk, the purpose of Tesla is to help expedite the move to sustainable transport and energy, obtained through electric vehicles and solar power. Tesla began production of its first car model, the Roadster sports car, in 2009. This was followed by the Model S sedan in 2012, the Model X SUV in 2015, the Model 3 sedan in 2017, and the Model Y crossover in 2020. The Model 3 is the all-time best-selling plug-in electric car worldwide and, in June 2021, became the first electric car to sell 1 million units globally. Tesla's global sales were 936,222 cars in 2021, a 87% increase over the previous year, and cumulative sales totaled 3 million cars as of August 2022. In October 2021, Tesla's market capitalization reached $1 trillion, the sixth company to do so in U.S. history.
Founding (2003–2004)
The company was incorporated as Tesla Motors, Inc. on July 1, 2003, by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning. These two guys were Eberhard and Tarpenning, who served as CEO and CFO, respectively. Eberhard said he wanted to build
"a car manufacturer that is also a technology company," with its core technologies as "the battery, the computer software, and the proprietary motor."
IaN Wright was Tesla's third employee, joining a few months later. In February 2004, the company raised $7.5 million in Series A funding, including $6.5 million from Elon Musk, who had received $100 million from the sale of his interest in PayPal two years earlier. Musk became the chairman of the board of directors and the largest shareholder in Tesla. J. B. Straubel joined Tesla in May 2004 as chief technical officer.A lawsuit settlement reached in September 2009 by Eberhard and Tesla allows all five -- Eberhard, Tarpenning, Wright, Musk, and Straubel -- to call themselves co-founders.
MODELS
Roadster (2005–2009)
Musk took an active role within the company and oversaw Roadster product design at a detailed level, but was not deeply involved in day-to-day business operations. The company's strategy was to start with a premium sports car aimed at early adopters and then move into more mainstream vehicles, including sedans and affordable compacts.In February 2006, Musk led Tesla's Series B venture capital funding round of $13 million, which added Valor Equity Partners to the funding team. Musk co-led the third, $40 million round in May 2006, which saw investment from prominent entrepreneurs including Google co-founders Sergey Brin and Larry Page, and former eBay President Jeff Skoll. A fourth round worth $45 million in May 2007 brought the total private financing investment to over $105 million.
Tesla's first car, the Roadster, was officially revealed to the public on July 19, 2006, in Santa Monica, California, at a 350-person invitation-only event held in Barker Hangar at Santa Monica Airport.
In August 2007, Eberhard was asked by the board, led by Elon Musk, to step down as CEO. Eberhard then took the title of "President of Technology" before ultimately leaving the company in January 2008. Co-founder Marc Tarpenning, who served as the Vice President of Electrical Engineering of the company, also left the company in January 2008. In August 2007, Michael Marks was brought in as interim CEO, and in December 2007, Ze'ev Drori became CEO and President. Musk succeeded Drori as CEO in October 2008. In June 2009, Eberhard filed a lawsuit against Musk for allegedly forcing him out.
Tesla began production of the Roadster in 2008.
Model S
The Model S is a five-door liftback sedan. Deliveries began on June 22, 2012. The car became the first electric vehicle to top the monthly sales ranking in any country when it achieved first place in the Norwegian new car sales list in September 2013. The Model S won the 2013 Motor Trend Car of the Year, the 2013 "World Green Car," Automobile magazine's 2013 "Car of the Year," Time magazine's "Best 25 Inventions of the Year 2012," as well as the 2019 Motor Trend "Ultimate Car of the Year."
Model X
The Tesla Model X is a mid-size crossover SUV. It is offered in 5-, 6-, and 7-passenger configurations. The Model X was developed from the full-sized sedan platform of the Model S. The rear passenger doors open vertically with an articulating "falcon-wing" design.Deliveries started in September 2015. In 2016, after one full year on the market, the Model X ranked seventh among the world's best-selling plug-in cars. The United States is its main market, with an estimated 57,327 units sold through September 2018.
Model 3
The Model 3 is a four-door fastback sedan. Tesla unveiled the Model 3 on March 31, 2016. Potential customers began reserving spots earlier that day with a refundable deposit. One week after the unveiling, Tesla reported over 325,000 reservations.Since March 2020, the Model 3 has been the world's best-selling electric car in history, and cumulative global sales passed the 1 million milestone in June 2021. The Model 3 has ranked as the world's best selling plug-in electric car for four consecutive years, from 2018 to 2021, and also as the best selling plug-in electric car in the United States since 2018. The Model 3 also set records in Norway and the Netherlands as the best-selling passenger car model in those countries in 2019.
Model y
The Model Y is a compact crossover utility vehicle. The Model Y is built on a platform that shares many components with the Model 3. The car has up to three rows of seats (for up to 7 people), 68 cubic feet (1.9 m3) of cargo space (with the second and third rows an EPA range of up to 326 miles (525 km).The Model Y was unveiled on March 14, 2019. Deliveries for the Model Y started on March 13, 2020. The Tesla Model Y is being manufactured at the Tesla Factory in Fremont, California, as well as in Giga Shanghai, China. A version of the Model Y is also expected to be produced at Giga Berlin once the factory is open.
Future products
Tesla Semi
The Tesla Semi is an all-electric Class 8 semi-trailer truck announced in November 2017. Musk confirmed that two variants would be available: one with 300 miles (480 km) and one with 500 miles (800 km) of range The Semi will be powered by four independent electric motors of the type used in the Tesla Model 3 and will include an extensive set of hardware sensors to enable it to stay in its own lane, a safe distance away from other vehicles, and later, when software and regulatory conditions allow, provide self-driving operation on highways. Musk also announced that the company would be involved in installing a solar-powered global network of Tesla Megachargers to make the Semi more attractive to potential long-haul customers. A 30-minute charge would provide 400 miles (640 km) of range.Musk initially said in 2017 that Semi truck deliveries would start in 2019 and that he would be selling 100,000 trucks a year, but deliveries were later delayed to 2021 and then 2023. Part of the reason for the delays, according to Musk, is that the Semi includes five times more battery cells than their passenger cars, and the battery supply is not yet sufficient for both Tesla cars and the Semi.
TESLA SEMI On November 16, 2017, Tesla unveiled the second generation Roadster as a surprise at the end of the event that introduced the Tesla Semi.Musk said that the new model will have a range of 620 miles (1,000 km) with the 200 kilowatt-hours (720 MJ) battery pack and will achieve 0–60 miles per hour (0–97 km/h) in 1.9 seconds; it also will achieve 0–100 miles per hour (0–161 km/h) in 4.2 seconds, and the top speed will be over 250 miles per hour (400 km/h). The SpaceX package will include cold air thrusters that will increase the speed even more. [134] The vehicle will have three electric motors, allowing for all-wheel drive and torque vectoring during cornering.At the time, the base price was set at $200,000, while the first 1,000 units (the Founder's Series) would sell for $250,000.[134] Reservations required a deposit of $50,000, and those who ordered the Founder's Series paid the $250,000 in full upon ordering. Those who made a reservation at the event were allowed a test drive (with a driver) in the prototype. Deliveries are expected to start in 2023.
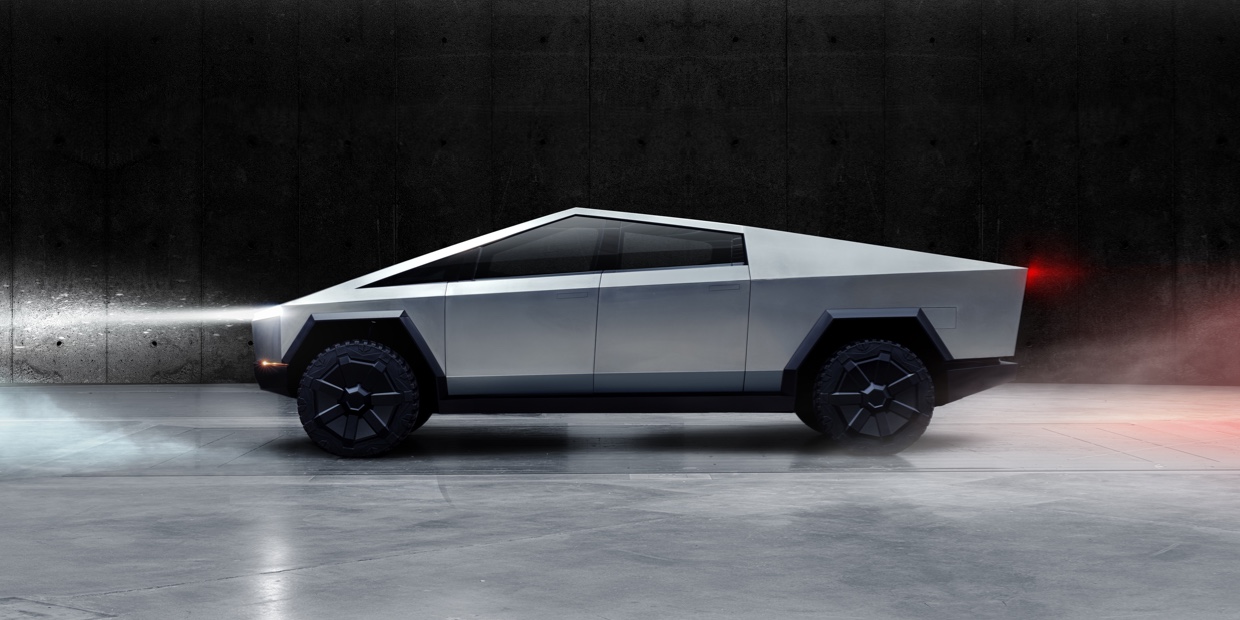
Cybertruck
The Cybertruck is a pickup truck unveiled on November 21, 2019. Production has been delayed past 2022, and as of January 2022, it is rumoured to be early 2023. The truck's design had a mixed reception, and some Wall Street analysts questioned whether American pickup truck buyers will have interest in the Cybertruck. On September 22, 2020, Musk revealed roughly 600,000 Cybertruck preorders. James Goodwin, chief executive of ANCAP, said in 2019 that the design of the Cybertruck could pose safety risks, saying that the front "would look like it’s not very forgiving." After the Cybertruck's unveiling, Musk announced that the Tesla Cyberquad, an electric four-wheel quad bike revealed alongside the Cybertruck, would be an optional accessory for Cybertruck buyers.
The Original Roadster
Main article: Tesla Roadster (First Generation)
The only discontinued Tesla vehicle model is the original Tesla Roadster. The Roadster was a two-seater sports car, evolved from the Lotus Elise chassis, that was produced from 2008 to 2012. The Roadster was the first highway legal serial production all-electric car to use lithium-ion battery cells and the first production all-electric car to travel more than 200 miles (320 km) per charge. It is also the first production car to be launched into space; it was carried into a Mars-crossing orbit by a Falcon Heavy rocket test flight on February 6, 2018.
Technology
Tesla develops many components in-house, such as batteries, motors, and software.
Vehicle batteries Tesla vehicle chassis, as seen in the Model S and X, with visible battery.
Tesla was the first automaker to use batteries containing thousands of small, cylindrical, lithium-ion commodity cells like those used in consumer electronics. Tesla uses a version of these cells that is designed to be cheaper to manufacture and lighter than standard cells by removing some safety features; according to Tesla, these features are redundant because of the advanced thermal management system and an intumescent chemical in the battery to prevent fires.
The batteries are placed under the vehicle floor. This saves interior and trunk (boot) space but increases the risk of battery damage by debris or impact (see crashes and fires). After two vehicle fires in 2013 due to road debris, the Model S was retrofitted with a multi-part aluminium and titanium protection system to reduce the possibility of damage.
In 2016, former Tesla CTO J.B. Straubel expected batteries to last 10-15 years and discounted using electric cars to charge the grid with vehicle-to-grid because the related battery wear outweighed the economic benefit. He also preferred recycling over re-use for grid once they reach the end of their useful life for vehicles. In 2019, Tesla launched its battery recycling operation at Giga Nevada.
Panasonic is Tesla's supplier of cells in the United States and cooperates with Tesla in producing cylindrical 2170 batteries at Giga Nevada. As of January 2021, Panasonic has the capacity to produce 39 GWh per year of batteries at Giga Nevada. Tesla's battery cells used in Giga Shanghai are supplied by Panasonic and Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL), and are the more traditional prismatic (rectangular) cells used by other automakers.
Battery research
Tesla invests in lithium-ion battery research. Starting in 2016, the company established a 5-year battery research and development partnership at Dalhousie University in Nova Scotia, Canada, with lead researcher Jeff Dahn. Tesla acquired two battery companies: Maxwell Technologies, acquired for over $200 million but sold in 2021, and Hibar Systems.
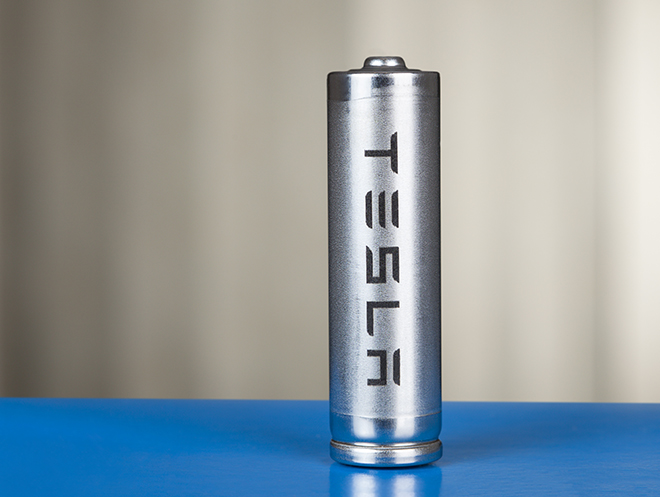
During Tesla's Battery Day event on September 22, 2020, Tesla announced the next generation of batteries, featuring a tab-less battery design to increase the range and decrease the price of Tesla vehicles. The new battery is named the "4680" in reference to its dimensions: 46 millimetres (1.8 in) wide by 80 millimetres (3.1 in) tall. Two weeks before Battery Day, Tesla paid a total of $3 to buy several battery manufacturing patent applications from Springpower International, a small Canadian battery company.
Tesla predicted that the new batteries would be up to 56% cheaper and would allow cars to travel 54% further.The company said this would be achieved by a more efficient production process, new battery design, cheaper resources for the anode and cathode, and better integration into the vehicle. Business analysis company BloombergNEF estimated Tesla's battery pack price in 2021 at $112 per kWh, versus an industry average of $132 per kWh. As of December 2021, BloombergNEF estimates the industry as a whole will reach $100 per kWh in 2024. The United States Department of Energy estimated in 2020 that with battery prices at $100 per kWh, electric cars would be the same cost to purchase as comparable gasoline-powered cars, which would accelerate the sales of electric cars.
Motors
Tesla makes two kinds of electric motors. Its oldest design in production is a three-phase, four-pole alternating current induction motor with a copper rotor (which inspired the Tesla logo), which is used as the rear motor in the Model S and Model X. Newer, higher-efficiency permanent magnet motors are used in the Model 3, Model Y, the front motor of 2019-onward versions of the Model S and X, and are expected to be used in the Tesla Semi. The permanent magnet motors increase efficiency, especially in stop-start driving.
Autopilot
Autopilot is an advanced driver-assistance system developed by Tesla. The system requires active driver supervision at all times... All Tesla vehicles have been equipped with sensors (initially, hardware version 1 or "HW1") and software to support Autopilot since September 2014.Tesla upgraded its sensors and software in October 2016 ("HW2") to support full self-driving in the future. HW2 includes eight cameras, twelve ultrasonic sensors, and forward-facing radar. HW2.5 was released in mid-2017, and it upgraded HW2 with a second graphics processing unit (GPU) and, for the Model 3 only, a driver-facing mera. [269] HW3 was released in early 2019 with an updated and more powerful computer, employing a custom Tesla-designed system on a chip. In April 2019, Tesla announced that all of its cars will include Autopilot software (defined as just Traffic-Aware Cruise Control and Autosteer (Beta)) as a standard feature moving forward. Full self-driving software (Autopark, Navigate on Autopilot (Beta), Auto Lane Change (Beta), Summon (Beta), Smart Summon (Beta), and future abilities) is an extra-cost option.
Full Self-Driving
Full Self-Driving (FSD) is an optional extension of Autopilot that is promoted as having the ability to perform fully autonomous driving in the future.At the end of 2016, Tesla expected to demonstrate full autonomy by the end of 2017, which as of July 2022 has not occurred. The first beta version of the software was released on October 22, 2020, to a small group of testers. The release of the beta has renewed concern regarding whether the technology is ready for testing on public roads. The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) has called for "tougher requirements" for any testing of Autopilot on public roads.
Tesla's approach to achieving full autonomy is different from that of other companies. Whereas Waymo, Cruise, and other companies are relying on highly detailed (centimeter-scale) three-dimensional maps, lidar, and cameras, as well as radar and ultrasonic sensors in their autonomous vehicles, Tesla's approach is to use coarse-grained two-dimensional maps and cameras (no lidar) as well as radar and ultrasonic sensors. Tesla claims that although its approach is much more difficult, it will ultimately be more useful because its vehicles will be able to self-drive without geofencing concerns. Tesla's self-driving software has been trained on over 20 billion miles of driving by Tesla vehicles as of January 2021. Tesla also designed a self-driving computer chip that has been installed in its cars since March 2019.
Most experts believe that Tesla's approach of trying to achieve full self-driving by eschewing lidar and high-definition maps is not feasible. In March 2021, according to a letter that Tesla sent to the California Department of Motor Vehicles about FSD's capability (acquired by PlainSite via a public records request), Tesla stated that FSD is not capable of autonomous driving and is only at Society of Automotive Engineers Level 2 automation. In a May 2021 study by Guidehouse Insights, Tesla was ranked last for both strategy and execution in the autonomous driving sector. In October 2021, the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) called on Tesla to change the design of its Autopilot to ensure it cannot be misused by drivers, according to a letter sent to Musk.
Glass
In November 2016, the company announced the Tesla Glass Technology Group. The group produced the roof glass for the Tesla Model 3. It also produces the glass used in the Tesla Solar Roof solar shingles.
OTHER SERVICES WERE
OTHER SERVICES WERE Tesla receives service revenue from its vehicle customers after their initial purchase; these revenues reached $1.47 billion in 2022 Q2. As of August 2020, those services include vehicle servicing, charging, insurance, software upgrades, and improved connectivity. In July 2021, Tesla will make full self-driving available as a monthly subscription. Future services that have been discussed include paying for a Wi-Fi hotspot in the car and the Tesla Robotaxi network.
Charging
Supercharger network
Tesla Supercharger: In 2012, Tesla began building a network of 480-volt fast-charging Supercharger stations. As of June 2022, Tesla operates 36,165 superchargers in 3,971 stations worldwide (an average of 9 chargers per station). The Supercharger is a proprietary direct current (DC) technology that provides up to 250 kilowatts (kW) of power. All Tesla cars except the first-generation Roadster come standard with hardware to charge at Superchargers. The navigation software in Tesla cars can recommend the fastest route for long-distance travel, incorporating charging stops.
destination charging location network
In 2014, Tesla launched the "Destination Charging Location" network by providing chargers to hotels, restaurants, shopping centers, and resorts (and other locations where Tesla owners may spend an hour or more) to provide on-site vehicle charging at twice the power of a typical home charging station.Destination chargers are installed free of charge by Tesla-certified contractors; the locations were originally required to provide the electricity at no cost to their customers. As of August 2022, locations with six or more destination chargers may start charging for electricity. All destination chargers appear in the in-car navigation system.
Software updates and upgrades
Tesla vehicles' software is regularly updated over-the-air when new software and firmware versions are released. This allows the cars to remain up-to-date and improve after purchase. Tesla also offers the option to unlock features in the car through over-the-air software upgrades after purchase. Available upgrades include basic Autopilot, full self-driving, an acceleration boost (for Model 3 owners), and rear-heated seats (for Model 3 owners).
Connectivity: All Tesla cars come with "Standard Connectivity," which provides navigation using a cellular connection and the following only over Wi-Fi or Bluetooth: internet browsing, music streaming (with a paid subscription), and, when parked, video streaming and "caraoke." "Premium Connectivity" adds cellular access to those features and also provides live traffic and satellite maps for navigation.
Vehicle servicing
Tesla's service strategy is to service its vehicles first through remote diagnosis and repair. If it is not possible to resolve a problem remotely, customers are referred to a local Tesla-owned service center or a mobile technician is dispatched. Tesla has said that it does not want to make a profit on vehicle servicing, which has traditionally been a large profit centre for most auto dealerships.
In 2016, Tesla recommended having any Tesla car inspected every 12,500 miles or once a year, whichever comes first. In early 2019, the manual was changed to say: "Your Tesla does not require annual maintenance and regular fluid changes," and instead it recommends periodic servicing of the brake fluid, air conditioning, tires, and air filters. & Insurance
FACILITIES
United States
Tesla Fremont Factory, Gigafactory Nevada, Gigafactory New York, and Gigafactory Texas
TESLA was founded in San Carlos, California. In 2010, Tesla moved its corporate headquarters and opened a powertrain development facility in Palo Alto.
Tesla's first retail store was opened in 2008 in Los Angeles, followed by others in major U.S. cities. As of June 2022, Tesla operates 196 stores and galleries in the United States,has stores and galleries in 34 other countries, and has 655 service centres globally.
Tesla's first assembly plant occupies the former NUMMI plant in Fremont, California, known as the Tesla Fremont Factory. General Motors opened the factory in 1962, and it has been run by a joint venture of GM and Toyota since 1984.The original factory was closed in 2010, and it was acquired by Tesla the same year.
Gigafactory in Nevada in 2019
And they were some other GIGAFACTORIES IN SHANGAI , GERMANY , AUSTRALIA
PARTNERS
Panasonic
Panasonic Energy Company President Naoto Noguchi presented Tesla CTO JB Straubel with the first lithium-ion cells from Panasonic's facility in Suminoe-ku, Osaka, Japan, in 2010.
In January 2010, Tesla and battery cell maker Panasonic announced that they would together develop nickel-based lithium-ion battery cells for electric vehicles. [364] The partnership was part of Panasonic's $1 billion investment over three years in facilities for lithium-ion cell research, development, and production.
Beginning in 2010, Panasonic invested $30 million for a multi-year collaboration on new battery cells designed specifically for electric vehicles. [366] In July 2014, Panasonic reached a basic agreement with Tesla to participate in battery production at Gigafactory Nevada.
Tesla and Panasonic also collaborated on the manufacturing and production of photovoltaic (PV) cells and modules at the Giga New York factory in Buffalo, New York. [305] The partnership started in mid-2017 and ended in early 2020, before Panasonic exited the solar business entirely in January 2021.In March 2021, the outgoing CEO of Panasonic stated that the company plans to reduce its reliance on Tesla as their battery partnership evolves.
Other current partners
In September 2020, Tesla signed a sales agreement with Piedmont Lithium to buy high-purity lithium ore for up to ten years,[371] specifically to supply "spodumene concentrate from Piedmont's North Carolina mineral deposit".
Tesla also has a range of minor partnerships, for instance working with Airbnb and hotel chains to install destination chargers at selected locations.
Former partners, Daimler AG
The Mercedes-Benz B-Class Electric Drive used a Tesla-supplied battery pack.
Daimler AG and Tesla began working together in late 2007. On May 19, 2009, Daimler bought a stake of less than 10% in Tesla for a reported $50 million. As part of the collaboration, Herbert Kohler, vice president of E-Drive and Future Mobility at Daimler, took a Tesla board seat. On July 13, 2009, Daimler AG sold 40% of its acquisition to Aabar. AAbar is an investment company controlled by the International Petroleum Investment Company (IPIC), which is owned by the government of Abu Dhabi. In October 2014, Daimler sold its remaining holdings for a reported $780 million.Tesla supplied battery packs for Freightliner Trucks' Custom Chassis electric van in 2010. The company also built electric-powertrain components for the Mercedes-Benz A-Class E-Cell, with 500 cars planned to be built for trial in Europe beginning in September 2011.
Tesla produced and co-developed the Mercedes-Benz B250e's powertrain, which ended production in 2017. [384]The electric motor was rated at 134 hp (100 kW) and 230 pound-force feet (310 Nm), with a 36 kWh (130 MJ) battery. The vehicle had a driving range of 200 km (124 mi) with a top speed of 150 km/h (93 (93 mph). [Daimler Division Smart produced the Smart ED2 cars from 2009 to 2012, whichhad a 14-kilowatt-hour (50 MJ) lithium-ion battery from TeslA.
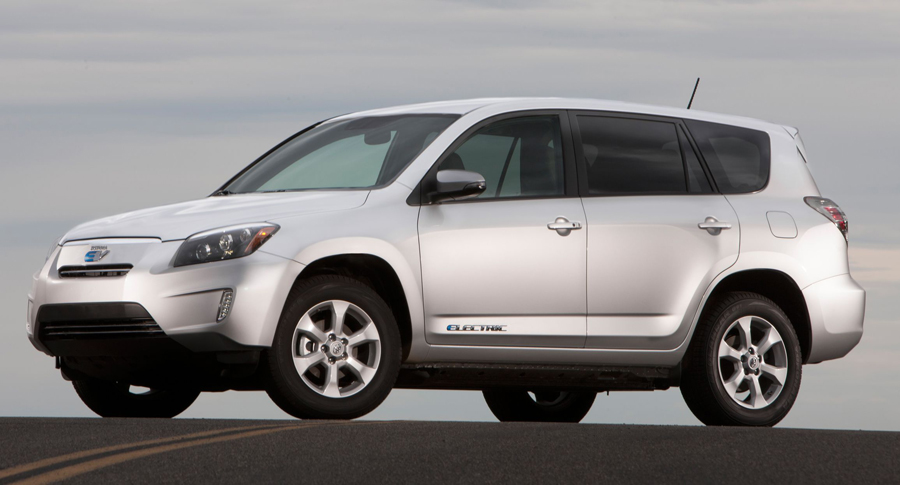
Toyota
Toyota RAV4 EV, which used A Tesla-supplied battery and powertrain components
In May 2010, Tesla and Toyota announced a deal in which Tesla purchased the former NUMMI factory from Toyota for $42 million, Toyota purchased $50 million in Tesla stock, and the two companies collaborated on an electric vehicle.
In July 2010, the companies announced they would work together on a second generation Toyota RAV4 EV. The vehicle was unveiled at the October 2010 Los Angeles Auto Show and 35 pilot vehicles were built for a demonstration and evaluation programme that ran through 2011. Tesla supplied the lithium metal-oxide battery and other powertrain components , based on components from the Roadster.
The production version was unveiled in August 2012, using a battery pack, electronics, and powertrain components from the Tesla Model S sedan (also launched in 2012). The RAV4 EV had a limited production run which resulted in just under 3,000 vehicles being produced before it was discontinued in 2014.
Mobileye
Tesla Autopilot
Initial versions of Autopilot were developed in partnership with Mobileye beginning in n 2014. Mobileye ended the partnership on July 26, 2016, citing "disagreements about how the technology was deployed."
AND IN LATER POSTS I'M GOING TO TALK ABOUT THE TECH BEHIND THE SELF DRIVING CARS AND THE COMPLEXITY BEHIND THE MAKING CUTTING EDGE TECH IN TESLA INC... LIKE motors and battery pack's
Thank u for spending ur valuable time
your's - 8BITPOD

















Comments
Post a Comment